5.1. Overview#
5.1.1. What is a Database?#
A database stores data relating to a particular subject. For example, you can have a database storing all the information on staff in a company.
Databases store data as a collection of relations (tables). There are usually relationships between these relations in the database.
Below is an example of a shopping database.
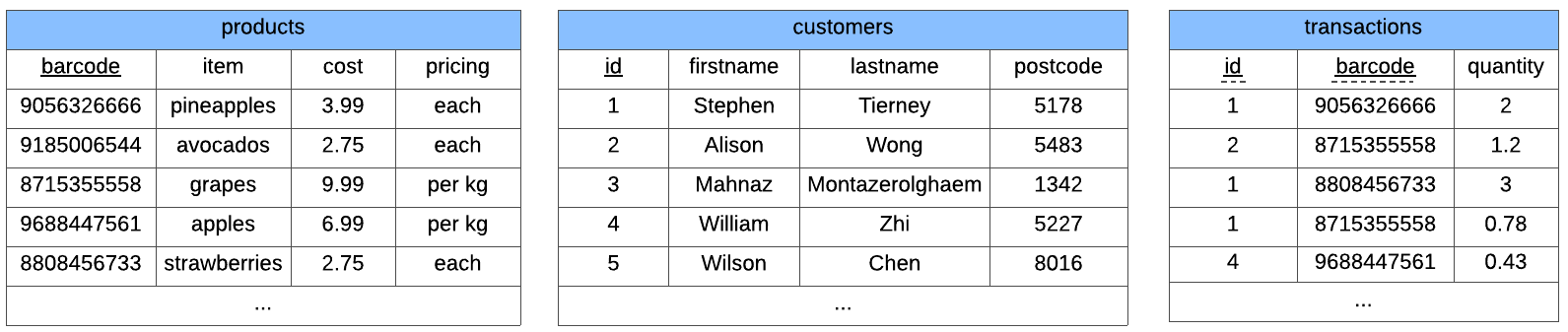
In this database, we have 3 tables.
The customers table tells us about the customers that come to the shop
The products table tells us about the items that the shop is selling
The transactions table tells us which customers have bought which items, and how much they have purchased.
5.1.2. Querying a Database#
To extract information from a database we construct a query.
A query is an instruction that tells the database what to do. For example, we can get a database to display a table, or we can tell the database to add new data.
To give our instructions to the database in a way it can understand, we need to formulate our query with a particular structure. For this, we will be using SQL (Structured Query Language). Like Python, SQL has its own rules for how you should write commands.
Here is an example of a query that displays the customers table.
SELECT *
FROM customers;